Kinetic Switches - A Complete Guide
Kinetic

In recent years, the advancement of technology has brought forth numerous innovations in the field of electrical control systems. One such remarkable development is the emergence of kinetic switches, which have revolutionized the way we interact with our electrical devices. Kinetic switches offer a convenient and efficient means of controlling power, providing a seamless transition from traditional mechanical switches. In this article, we will delve into the history of kinetic switches, explore their inner workings, and examine the various components and advancements associated with this technology. Additionally, we will shed light on the prominent manufacturer, EnerJ, and their contributions to this groundbreaking field.
The History of Kinetic Switches
The roots of kinetic switches can be traced back to the early 20th century when the first mechanical switches were introduced. These switches relied on physical contact, requiring manual operation to control the flow of electricity. While functional, these switches were prone to wear and tear, resulting in eventual failure and limited lifespan.
Over time, advancements in materials science and electronics led to the development of solid-state switches, which used semiconductors to control electrical current. These switches offered improved reliability and durability, but they still required direct physical interaction, whether through a button or a touch-sensitive surface.
The concept of kinetic switches emerged as a response to the need for more efficient and user-friendly control mechanisms. Kinetic switches eliminate the need for direct physical contact by utilizing motion and gesture-based sensing technologies to activate and control electrical devices.
How Kinetic Switches Work
Kinetic switches operate on the principle of motion detection and gesture recognition. They employ various sensor technologies, such as infrared (IR) sensors, capacitive sensors, or motion sensors, to detect movement or specific gestures made by the user. These sensors are integrated into the switch housing or installed in the surrounding environment.
When a user approaches a kinetic switch, the built-in sensors detect their presence. The switch can then interpret the user's intended action based on predefined gestures or commands. For example, a simple wave of the hand can turn a light on or off, while a rotating gesture might adjust the brightness level. These gestures are converted into electrical signals that are processed by the switch's internal circuitry, which subsequently controls the power supply accordingly.
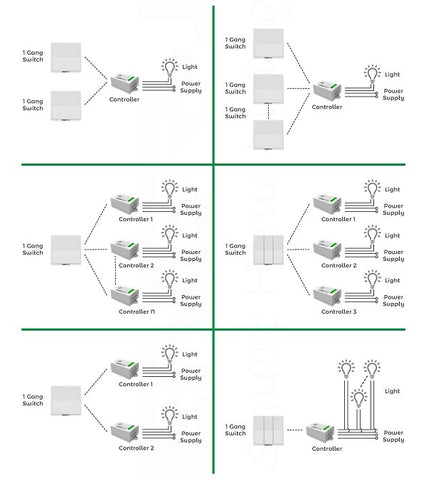
Components of Kinetic Switches
WiFi Receivers - In order to enable wireless communication and connectivity, many kinetic switches come equipped with WiFi receivers. These receivers allow the switch to connect to a local network, enabling remote control and integration with smart home systems. WiFi receivers facilitate the transmission of control signals and enable seamless interaction between the user and their electrical devices.
Non-Dimmable Switches - Non-dimmable kinetic switches are designed to control devices with fixed output levels, such as simple on/off operations. These switches are suitable for applications where a specific level of power output is required without the need for adjustable brightness or intensity.
Dimmable Switches - Dimmable kinetic switches provide the ability to control the brightness or intensity of compatible devices. These switches incorporate additional circuitry and components that allow for precise adjustment of power output. Dimmable switches are commonly used for controlling lighting fixtures, providing customizable illumination levels to suit different moods and requirements.
Smart WiFi Receivers - Smart WiFi receivers are advanced components found in certain kinetic switches. They enable seamless integration with smart home systems, such as voice assistants or mobile applications. With smart WiFi receivers, users can control their electrical devices remotely, create automated schedules, and even receive real-time energy consumption data

EnerJ
EnerJ is a renowned manufacturer that has made significant contributions to the field of kinetic switches. Established in 2005, the company has been at the forefront of developing innovative solutions for energy-efficient control systems. EnerJ's expertise lies in the integration of motion and gesture recognition technologies into their kinetic switches, resulting in enhanced user experiences and optimized energy consumption.
With a strong focus on research and development, EnerJ has introduced a wide range of kinetic switches that cater to various applications and customer preferences. Their product lineup includes both non-dimmable and dimmable switches, ensuring compatibility with diverse electrical devices.
EnerJ's commitment to sustainability is evident in their smart WiFi receivers, which allow users to monitor and manage energy usage effectively. By empowering users with data-driven insights, EnerJ promotes responsible energy consumption, ultimately contributing to a greener and more sustainable future.
See the full range of Kinetic Switches we stock here!

Conclusion
Kinetic switches have paved the way for a new era of electrical control systems, offering a seamless and intuitive approach to interact with our devices. From their humble beginnings as mechanical switches to the integration of motion detection and gesture recognition technologies, the evolution of kinetic switches has been remarkable.
With their ability to eliminate physical contact, wireless connectivity, and compatibility with smart home systems, kinetic switches provide unparalleled convenience and energy efficiency. Manufacturers like EnerJ continue to drive advancements in this field, ensuring a brighter and smarter future for electrical control systems.
As kinetic switches become increasingly prevalent in homes and commercial spaces, they hold the potential to transform the way we interact with electricity, enhancing comfort, convenience, and sustainability in our daily lives.
Kinetic Switches FAQ
A kinetic switch is an innovative electrical control device that utilizes motion detection and gesture recognition technologies to activate and control electrical devices. It eliminates the need for physical contact and offers a more convenient and intuitive way to interact with power sources.
Yes, kinetic switches are designed to be highly reliable. They are built with durable components and undergo rigorous testing to ensure longevity and consistent performance. With no physical contacts to wear out, kinetic switches offer enhanced reliability compared to traditional mechanical switches.
Programming a kinetic switch typically involves following the manufacturer's instructions. This often includes steps such as connecting the switch to a power source, setting up any required wireless connections, and configuring the switch's settings using provided software or mobile applications.
Wireless light switches, including kinetic switches, can operate without batteries by harnessing the energy generated from the user's kinetic motion or the mechanical energy generated when pressing the switch. This energy is converted into electrical power, eliminating the need for batteries or external power sources.
The range of a kinetic wireless switch depends on various factors, including the specific technology used and the environmental conditions. In general, most kinetic wireless switches have a range of several meters, allowing for control within a room or adjacent areas.
Yes, many kinetic switches are compatible with smart home systems such as Amazon Alexa. By integrating the switch with Alexa or other voice assistants, users can control their electrical devices using voice commands, adding an extra layer of convenience to their smart home setup.
To connect a kinetic switch to WiFi, you typically need to follow the manufacturer's instructions provided with the switch. This usually involves using a mobile application or accessing the switch's settings through a web portal. The process generally includes selecting the desired WiFi network, entering the network password, and completing the setup process within the application or web interface.
Smart switches themselves consume minimal electricity. However, some smart switches may have additional features or components, such as WiFi receivers, which may consume a small amount of power when in standby mode. Overall, the power consumption of smart switches is negligible compared to the devices they control.
The specific frequency of a kinetic switch depends on the technology used for wireless communication. While various frequencies can be employed, common frequencies for wireless kinetic switches include 2.4 GHz or 5 GHz, which are widely used for WiFi connectivity.
>RF (Radio Frequency) and Wi-Fi are both wireless communication technologies, but they differ in several aspects. RF encompasses a broad range of frequencies used for wireless communication, including technologies like Bluetooth and Zigbee. Wi-Fi, on the other hand, refers specifically to wireless networking using the IEEE 802.11 standard and typically operates in the 2.4 GHz or 5 GHz frequency bands.
>Yes, Wi-Fi signals can potentially interfere with RF signals, depending on the specific frequencies and the proximity of the devices. If devices using Wi-Fi and RF technologies operate in close proximity or within the same frequency range, there is a possibility of interference. Proper placement, configuration, and isolation techniques can help mitigate such interference and ensure optimal performance of both technologies.
